I keep seeing the same error in the news: you're 25 times more likely to end up in the hospital if you're unvaccinated! It's due to a misunderstanding of relative vs. absolute risk.
 |
| From Pixabay. |
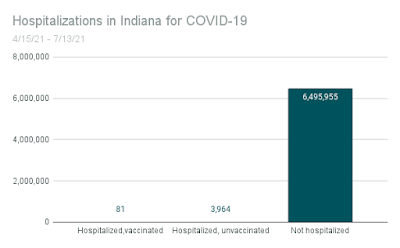
For readers who aren't familiar with the concept, I've made a visual aid based on actual figures from Indiana:
- Dates: April 15, 2021 through July 13, 2021
- Hospitalizations due to COVID: 4,045
- Percent of hospitalized COVID patients who were vaccinated: 2%
- Population of Indiana: 6,500,000
Going by the high portion of unvaccinated COVID patients, it makes it sound like you're 50 times more likely to go to the hospital if you haven't had the shot. That's relative risk. If you're at a high risk of getting a bad case of COVID, that's meaningful. But if you aren't, you're reducing a tiny risk to a minuscule risk.
I didn't forget to add the first two columns--they just don't show up in the context of a population of 6.5 million. Likewise, the 655 people who've died over the past 90 days. I'm not trying to make it seem trivial that people have died or gone to the hospital. Rather, it's to give a more realistic picture of risk. Doctors are often in the news or on YouTube telling about the horrors of COVID--but their perspective seems like it suffers from availability bias: they see suffering all day, and almost all of the suffering is among unvaccinated people. But they're homed in on a tiny group of people.Imagine the homeless for a moment. The vast majority of them are men. If you're a man, would you take an experimental medication that could help you avoid becoming homeless--maybe a medication that makes people more conscientious? It might be worth it for someone at high risk of becoming homeless, but again, for most it would reduce a tiny risk to a minuscule one.
The focus has been on illness for the past 18 months to the exclusion of almost everything else. In a state that has the 14th highest deaths per capita, here's a graph of COVID numbers for those past 18 months.

Comments