 |
The Badlands of South Dakota.
|
An article today in The Spectator (US and UK) decries the lack of regulations in South Dakota to deal with the coronavirus, calling it a "failed experiment." The author compares South Dakota's response, or lack of it, to Sweden--and then calls Sweden a failure, too. From this, he concludes that lack of coronavirus regulation allows rampant spreading of the disease, and implies that strict regulation controls it. Does it really--and are those devil-may-care Swedes and South Dakotans about to drop like flies? Let's look at their numbers and compare them not to perfection, but to some places that have had strict regulations to get an idea how well the regulations might be working. The article doesn't specify which measures should be mandated, so let's assume lockdowns.
I'll avoid using out-of-the-way places and epicenters, since they would have low or high numbers no matter what they did. And since there's been so much variation in how deaths are reported and what constitutes a case, and since lockdowns themselves have effects, I'm going to look at excess deaths: deaths at a number above what would normally be expected for the time of year. Here's South Dakota's excess deaths from the CDC. (Click graphics to enlarge.)
The article also mentions North Dakota's similar lack of regulations, and they have had a spike in excess deaths.
What about other states that have not issued many regulations? South Dakota's neighbor Iowa never issued a stay at home order and had few closures. They have had some excess deaths, but not a spike in them.
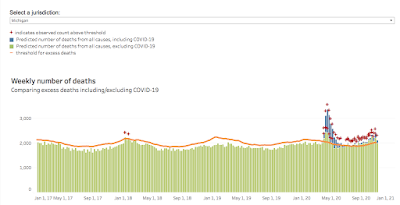
Now let's look at states that took a hard line: Michigan, Pennsylvania and California. These states are no longer under strict lockdowns, as those have been voided in court. Here's Michigan:
Pennsylvania:
California:
I've also looked at several states plus New York City and Washington DC. There are three common patterns: a big spike in excess deaths followed by few or no excess deaths (like Michigan and Pennsylvania), a middling number of excess deaths starting in spring and continuing to the present (like Iowa), and sudden surges (like the Dakotas).
In terms of excess deaths per million population, I'll be darned if I can see many patterns--and I made a list with every state. The most far-flung states (plus Puerto Rico) had among the lowest numbers; the least healthy and some small states near the epicenter of New York City had among the highest. South Dakota is about halfway in the middle. Here are the results for our six states; you can see the whole list
here.
Based on excess deaths per million, South Dakota isn't a failure, being in the middle of the pack. What about
Sweden--and
South Korea, for that matter, which also didn't have lockdowns, but did take less-strict measures?
Sweden spiked, then went into negative territory. South Korea never saw a big spike and COVID daily deaths remain in single digits--and it's a crowded country of over fifty million people. Their low numbers might have to do with low levels of diabetes and overweight, two common factors in COVID deaths, and their experience dealing with epidemics. How do these countries compare to others that had strict lockdowns--again, ignoring epicenters and out-of-the-way places?
First, note that this graph goes up to 100%, whereas the previous one showing Sweden and South Korea goes up to only 40%. France doesn't look bad for the summer, but they've had a resurgence in daily COVID deaths for the past month.
In fairness, Sweden is a somewhat out-of-the-way place and South Korea has less diabesity and more experience controlling epidemics. And we don't know how the other countries would have done without strict measures, nor are we at the end of the pandemic. So what can we figure out from these charts?
- If Sweden is an indication, a peak in excess deaths can sharply decline without a lockdown.
- Strict lockdowns haven't prevented second waves of excess deaths in France and Belgium.
- Michigan and Pennsylvania, which have have already had a sharp spike in excess deaths, haven't seen a second one (so far) with lockdowns off the table.
When someone says something is a failure, we need to ask, compared to what? Several places with strict lockdowns had spikes in excess deaths and two had second waves to boot. Quarantines for healthy people are novel and have no track record. There's no science behind them, which the let's-follow-the-science crowd keeps ignoring. If we're really following the science, we need to acknowledge that so far, we can't point to lockdowns as a reliable way of preventing excess deaths.








Comments